A new study in Cell Reports shows the first results obtained using z-Movi; ! Kamsma et al. used the z-Movi to measure the adhesion forces and kinetics of CD4+ T lymphocytes (CD4) to fibronectin in living conditions. They then investigated how these properties are influenced by interleukin-7 (IL-7), the main regulatory cytokine of CD4 cells. The results demonstrated that IL-7 accelerates CD4 adhesion but does not influence CD4 binding strength. Congratulations to all the authors!
Reprinted with permission from Cell Reports, 2018,24 (11), pp 3008-3016. Copyright 2018 Elsevier.
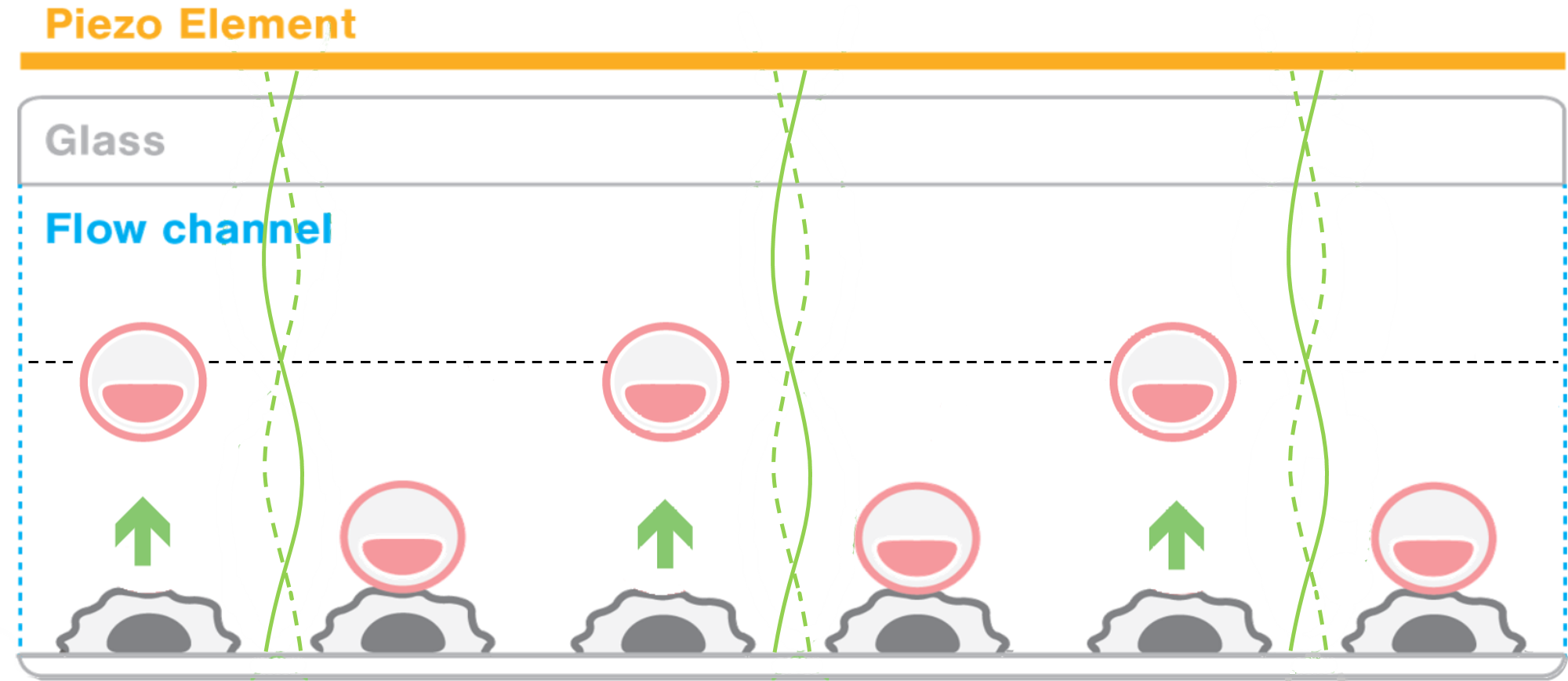
The z-Movi makes use of acoustic waves to exert well-controlled forces to hundreds of individual cells in parallel. Based on Acoustic Force Spectroscopy technology, it is the first system that can measure the interactions between single cells and their targets with high throughput.
The video shows multiple human CD4 cells as they are being subjected to a force ramp corresponding to forces ranging from 0 to 55 pN. Under the influence of these forces, we can observe the unbound and weakly-bound cells lifting off from their fibronectin targets. The authors distinguished three classes of cells: unbound, binding, and bound. Interaction strengths below 30 pN were identified for unbound cells, below 55 pN for transient binding and crawling cells, and from 55 pN to hundreds of piconewtons for bound cells.
Interested in using the z-Movi for your own experiments? Feel free to contact us for a demo or a quote.