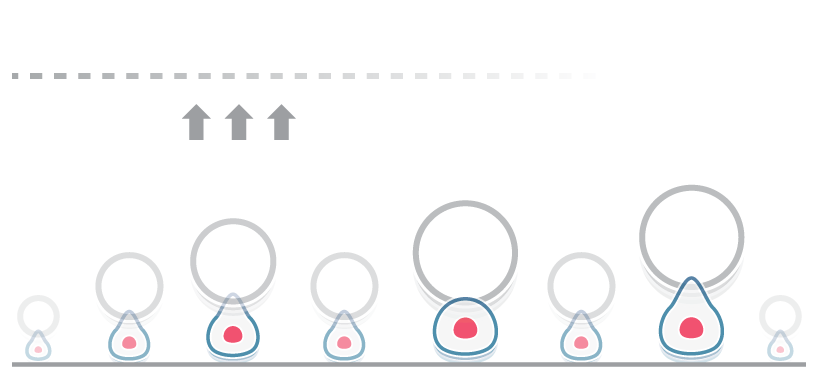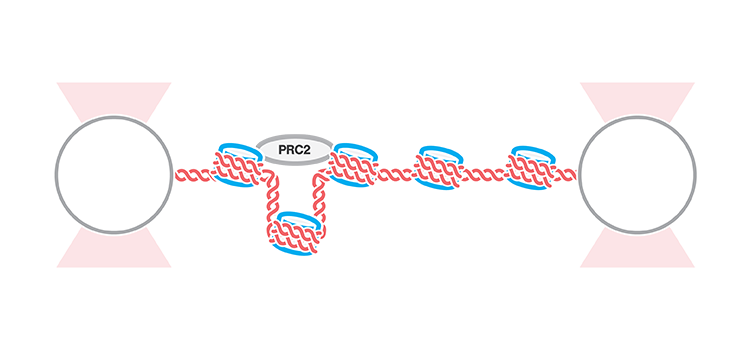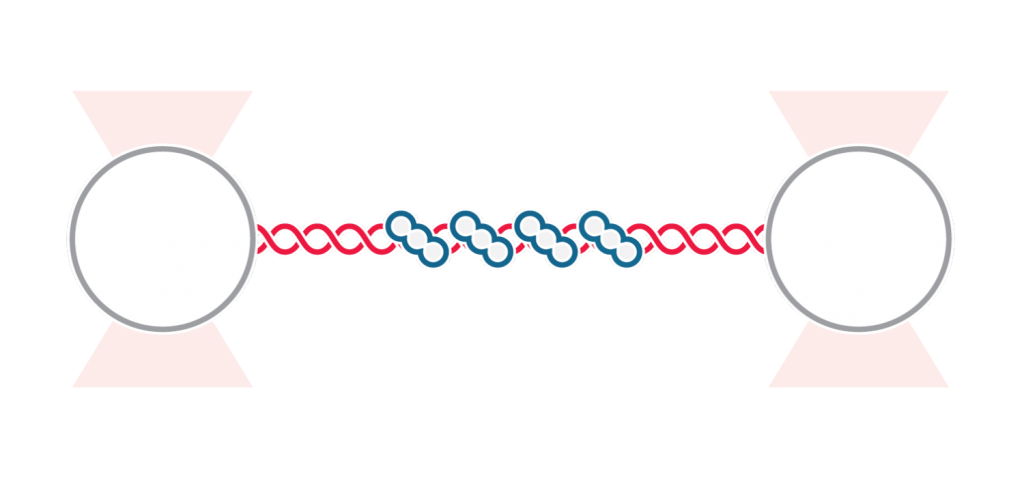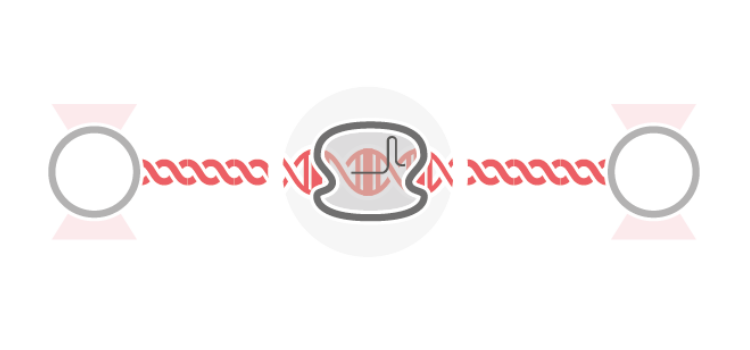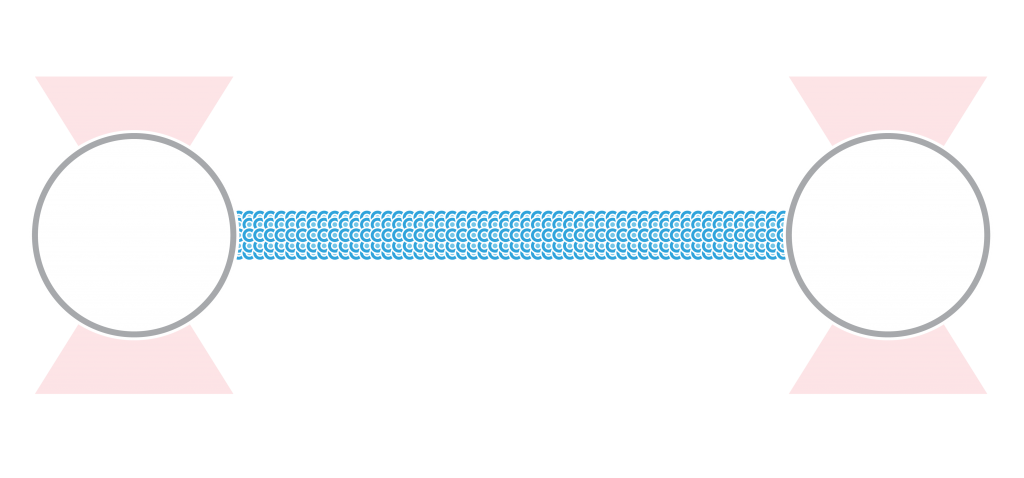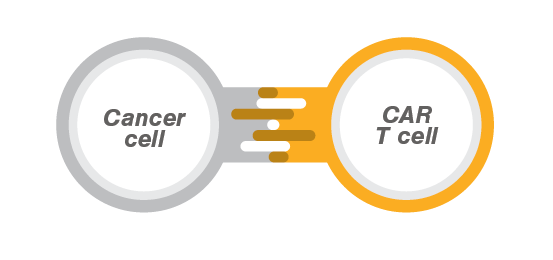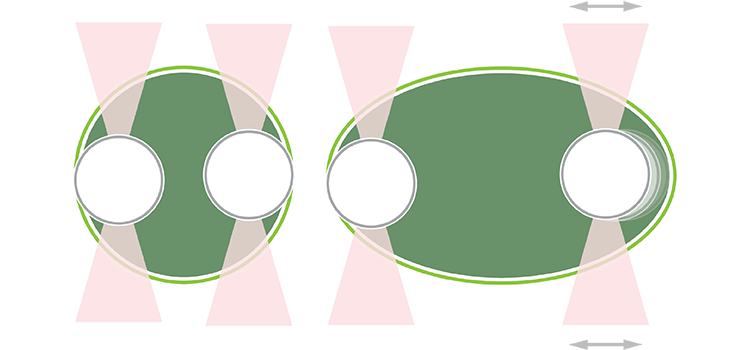
A recent publication in Science describes a new glass-like structural behavior that protein droplets can adopt, regulating their biochemical behavior as they age. Specifically, through rheological measurements using the C-Trap® optical tweezers, the researchers discovered material properties that may help cells respond to a dynamic molecular environment. The findings offer essential insights into the…
j.yeh16 February 2021